Describe the Structure of an Amino Acid
Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA carry genetic information which is read in cells to make the RNA and proteins by which living things function. The R group also known as a side chain is different for each.

General Structure Of A Amino Acid Download Scientific Diagram
Describe the characteristics of the structure its catabolic products and role in one or more metabolic pathways or function.
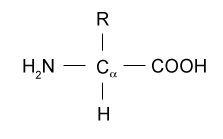
. An amino group a carboxyl group a hydrogen atom and a variable group symbolised by R. The simplest and smallest amino acid found in proteins is glycine for which the R-group is a hydrogen H. It is the R-group or side chain that makes each of the 20 amino acids unique.
In the centre of the amino acid is an assymetric carbon atom called the alpha carbon. The second one is a carboxyl group -OOOH. Describe the structure of the amino acid alanine.
The carbon atom of the carboxyl group has a free bond to bond to nitrogen of the other amino group that now also has a free bond. Scientists use the name amino acid because these acids contain both amino group and carboxyl-acid-group in their basic structure. Describe the structure of an amino acid including the importance of the side chain in determining properties of the amino acid.
The functions and structures of proteins can be annotated at three levels of resolution. This is the variable radical group and is different for every amino acid. Amino acids is made of amino group a carboxyl group a hydrogen atom and a side chain bonded to the central carbon atomThe side chainand its physical and chemical properties is what makes each amino acid different from the other.
Where might you expect to find these amino acids in a protein. One is an amine group -NH 2. Amino acids join together in an enzyme-catalysed condensation reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of.
The basic structure of an amino acid an amino acid consists of one central carbon. Atomic amino-acid AA and whole-protein. Amino acids are the monomers that make up proteins.
Why are some amino acids hydrophobic whereas others are hydrophilic. The primary repository of atomic-level information is the Protein Data Bank PDB which currently houses 160 thousand protein structures. All amino acids found in proteins have this basic structure differing only in the structure of the R-group or the side chain.
Select one of the amino acids. Each amino acid has the same fundamental structure which consists of a central carbon atom also known as the alpha α carbon bonded to an amino group NH 2 a carboxyl group COOH and to a hydrogen atom. The α carbon carboxylic acid and amino groups are common to all amino acids so the.
Basic Structure of an Amino Acid. Where might you expect to find these amino acids in a protein. Ah hydrogen carb oxalic acid group in the Mean group and another group thats different from all these usually different to say sometimes called the our group or sometimes called the side chain.
Structure of an Amino Acid. Structures of 20 Amino acids Classification of Amino acids Classification based on the structure 1. At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the α carbon and attached to it are four groups a hydrogen a carboxylic acid group an amine group and an R-group sometimes referred to as a variable group or side chain.
PLEASE MARK AS BRAINLIEST. All amino acids contain a carbon atom in the middle of the molecule the alpha-carbon. Hydroxyl group containing amino acids.
Nine of these are essential amino acids in humans because the human body cannot produce them and we obtain them from our diet. There are 20 different amino acids and they all share the same general structure. Describe the structure of an amino acid including the importance of the side chain in determining properties of the amino acid.
Those amino acids whose ZR group contains a chain of carbon atoms a. This R group makes the amino acid unique. A water molecule is removed by releasing an OH from carboxyl group of one amino acid and hydrogen from the amino group of another amino acid.
As we mentioned there are 20 common amino acids present in proteins. Its which are bonded. 4 marks - there is a central C atom - an NH2 amine group - a COOH carboxyl group opposite the amine group - and a methyl group opposite the H OR displayed formula 4 marks.
Name the covalent bond between two adjacent amino acids in a chain of amino acids. Amino acids link together to form proteins. The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
This atom is surrounded by three chemical groups. Explain how the primary sequence of a protein is important in determining the secondary and tertiary. Mono amino mono carboxylic i.
All amino acids have a central carbon atom surrounded by a hydrogen atom a carboxyl group COOH an amino group NH2 and an R-group. The amino acid that I chose was lysine which is an essential amino acid. The well-known structure of the DNA double helix allows this information to be copied and passed on to the next generation.
All amino acids have the same basic structure shown in Figure 21. For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains A and B shown in diagram below. The third group is denoted by R.
The R can represent one of 20 different side chains. Val Leu Ile iii. The insulin molecule shown here is cow insulin although its structure is similar to that of human insulin.
The amino acid that I chose was lysine which is an essential amino acid. An amino acid consists of a central or alpha carbon atom attached to an amino group NH2 a carboxylic acid group COOH a hydrogen atom and a variable side group called the R group. This carbon is covalently bonded to four different groups.
Amino acids are molecules used to build proteins. In the aqueous environment of the cell the both the amino group and the. Why are some amino acids hydrophobic whereas others are hydrophilic.

Amino Acids Structure Classification Properties With Videos Examples

Comments
Post a Comment